What causes earthquakes? A geologist explains where they’re most common and why
Sep 13, 2023

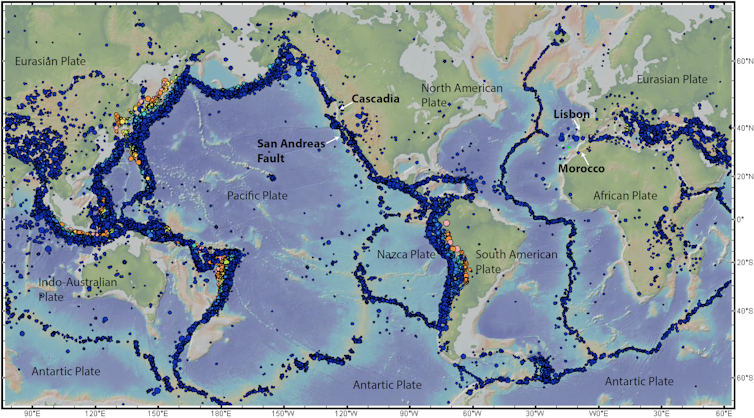
Earthquakes, large and small, happen every single day along zones that wrap around the world like seams on a baseball. Most don’t bother anybody, so they don’t make the news. But every now and then a catastrophic earthquake hits people somewhere in the world with horrific destruction and immense suffering.
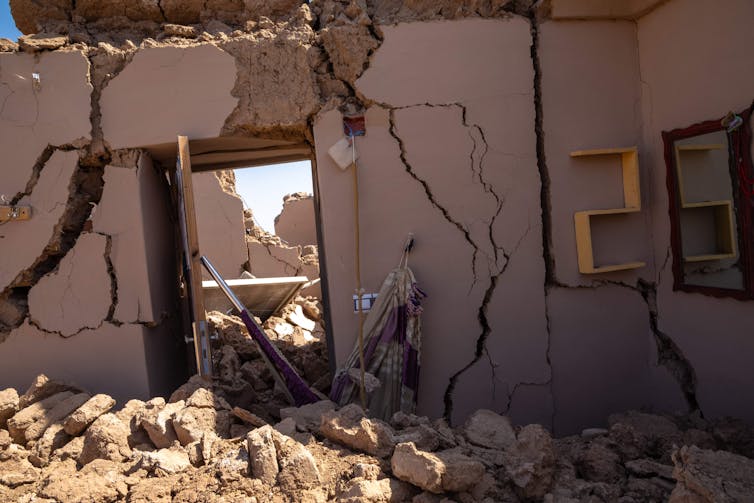
On Oct. 7, 2023, a 6.3 magnitude earthquake struck near the historic city of Herat, Afghanistan, leaving more than 1,000 people dead in the rubble, according to estimates. It was followed by another earthquake, just as powerful, on Oct. 11. A few weeks earlier, on Sept. 8, a 6.8 magnitude earthquake in the Atlas Mountains of Morocco shook ancient villages apart, killing nearly 3,000 people. In February 2023, a large area of Turkey and Syria was devastated by two major earthquakes that hit in close succession.
As a geologist, I study the forces that cause earthquakes. Here’s why some seismic zones are very active while others may be quiet for generations before the stress builds into a catastrophic event.
Earth’s crust crashes into itself and pulls apart
Earthquakes are part of the normal behavior of the Earth. They occur with the movement of the tectonic plates that form the outer layer of the planet.
You can think of the plates as a more or less rigid outer shell that has to shift to allow the Earth to give off its internal heat.
USGS/GMRT
These plates carry the continents and the oceans, and they are continuously in slow-motion crashes with one another. The cold and dense oceanic plates dive under continental plates and back into Earth’s mantle in a process known as subduction. As an oceanic plate sinks, it drags everything behind it and opens a rift somewhere else that is filled by rising hot material from the mantle that then cools. These rifts are long chains of underwater volcanoes, known as mid-ocean ridges.
Earthquakes accompany both subduction and rifting. In fact, that is how the plate boundaries were first discovered.
In the 1950s, when a global seismic network was established to monitor nuclear tests, geophysicists noticed that most earthquakes occur along relatively narrow bands that either fringe the edges of ocean basins, as in the Pacific, or cut right down the middle of basins, as in the Atlantic.
They also noticed that earthquakes along subduction zones are shallow on the oceanic side but get deeper under the continent. If you plot the earthquakes in 3D, they define slablike features that trace the plates sinking into the mantle.

Jaime Toro, CC BY-ND
An experiment: How an earthquake works
To understand what happens during an earthquake, put the palms of your hands together and press with some force. You are modeling a plate boundary fault. Each hand is one plate, and the surface of your hands is the fault. Your muscles are the plate tectonic system.
Now, add some forward force to your right hand. You will find that it will eventually jerk forward when the forward force overcomes the friction between your palms. That sudden forward jerk is the earthquake.
Jaime Toro
Scientists explain earthquakes using what’s known as the elastic rebound theory.
Fast plates move at up to 8 inches (20 centimeters) per year, driven mostly by the oceanic slabs sinking at subduction zones. Over time, they become stuck to each other by friction at the plate boundary. The attempted motion deforms the plate boundary zone elastically, like a loaded spring. At some point, the accumulated elastic energy overcomes the friction and the plate jerks forward, causing an earthquake.
But the plate-driving forces do not stop, so the plate boundary starts to accumulate elastic energy again, which will cause another earthquake – perhaps soon or perhaps far in the future.
In the oceans, plate boundaries are narrow and well defined because the underlying rocks are very stiff. But within the continents, plate boundaries are often broad zones of deformed mountainous terrain crisscrossed by many faults. Those faults may persist for eons, even if the plate boundary becomes inactive. That is why sometimes earthquakes occur far from plate boundaries.
Earthquakes, fast and slow
The cyclic behavior of faults allows seismologists to estimate earthquake risks statistically. Plate boundaries with fast motions, such as the ones along the Pacific rim, accumulate elastic energy rapidly and have the potential for frequent large-magnitude earthquakes.
Slow-moving plate boundary faults take longer to reach a critical state. Along some faults, hundreds or even thousands of years can pass between large earthquakes. This allows time for towns to grow and for people to lose ancestral memory of past earthquakes.

Muhammad Balabuluki/Middle East Images/Middle East Images via AFP
The earthquake in Morocco is an example. Morocco is located on the boundary between the African and the Eurasian plates, which are slowly crashing into each other.
The huge belt of mountains that extends from the Atlas of North Africa to the Pyrenees, Alps and most of the mountains across southern Europe and the Middle East is the product of this plate collision. Yet because these plate motions are slow near Morocco, large earthquakes are not so frequent.
Afghanistan is more prone to earthquakes. It has numerous faults created by the collision of India against Eurasia. The Indian Plate, which is old and stiff, has been plowing into the southern margin of Eurasia for the past 40 million years. You can see evidence of this slow-moving collision in the way the mountain chains – and the earthquakes – wrap around either side of India.
Preparing for the big one
An important fact about catastrophic earthquakes is that, in most cases, the earthquakes don’t kill people – falling buildings do.
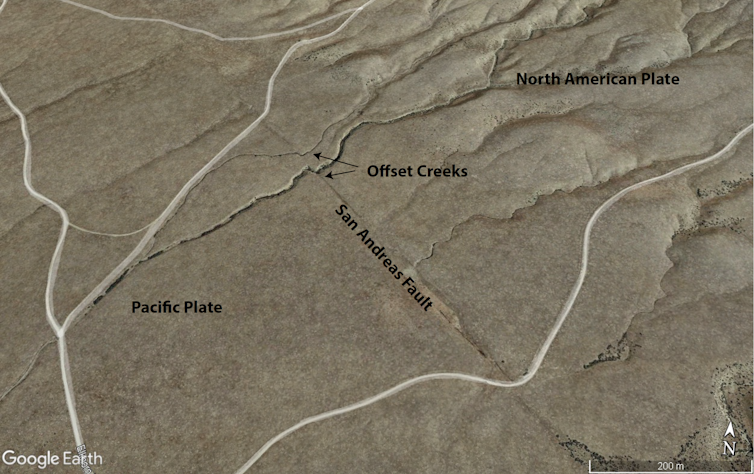
Most Americans have heard of California’s San Andreas Fault and the seismic risk to San Francisco and Los Angeles. The last major earthquake along the San Andreas Fault hit at Loma Prieta, in the San Francisco Bay area, in 1989. Its magnitude, 6.9, was comparable to that of the earthquake in Morocco, yet 63 people died compared with thousands. That’s largely because building codes in these earthquake-prone U.S. cities are now designed to keep structures standing when the Earth shakes.
The exceptions are tsunamis, the huge waves generated when an earthquake shifts the seafloor, displacing the water above it. A tsunami that hit Japan in 2011 had horrific consequences, regardless of the quality of engineering in coastal towns.
Unfortunately, earthquake scientists can’t predict exactly when an earthquake might occur; they can only estimate the hazard.
This article, originally published Sept. 13, 2023, has been updated with a powerful aftershock in Afghanistan.
![]()
Jaime Toro has received funding from NSF, USGS and DOE in the past.