A Rainforest Like No Other
Nov 23, 2021
There are few other places like Daintree rainforest in far north Queensland. Thought to be among the most ancient forests in the world, Daintree has many plants with lineages that scientists have traced back hundreds of millions of years to a time when several continents were joined together as Gondwana. All seven of the world’s oldest surviving fern species can still be found in Daintree, as well as 12 of the world’s 19 most primitive flowering plants.
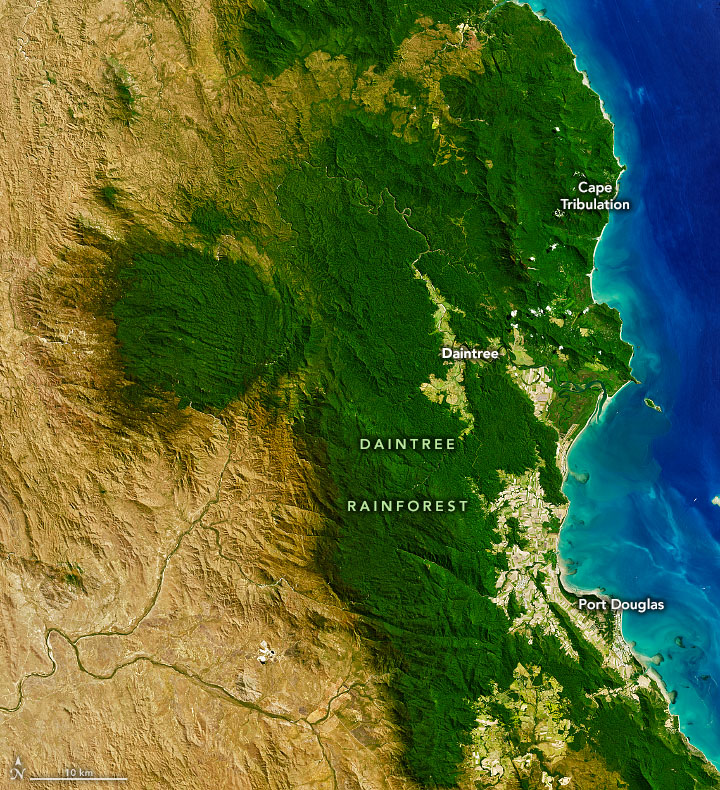
On September 5, 2019, the Operational Land Imager (OLI) on Landsat 8 captured this natural-color image of part of the rainforest. The steep escarpments and peaks of the Great Dividing Range play a key role in fueling the rain in Daintree. As moisture-laden winds blow in from the Coral Sea, orographic lifting pushes air up and over the mountains. In the process, water vapor cools, forms clouds, and produces rain. On average, higher-elevation parts of the rainforest receive more rain, especially on the eastern slopes of mountains.
Many of the species found in Daintree are exclusive to the area. For the 40 million years since Australia broke from the Gondwana, evolutionary processes have hummed along in geographic isolation, yielding unusual types of animals such as marsupials and monotremes. That long period of isolation, along with northern Queensland’s stable and mild climate and rugged topography, has resulted in remarkable biodiversity. This one ecosystem provides habitat for 65 percent of Australia’s fern species, 60 percent of its butterflies, and 50 percent of its birds.
Among the birds is the endangered southern cassowary—a large, flightless ratite with a blue head, two red wattles, and a distinctive dinosaur-like bony casque on its head. Cassowaries, the third largest type of bird in the world, have the helpful habit of distributing and seeding at least 70 different types of trees as they forage for fallen fruit.
In September 2021, the Queensland government returned ownership of Daintree National Park to the Eastern Kuku Yalanji, an indigenous group that has had a presence in Australia’s rainforests for at least 50,000 years. Daintree, Ngalba-bulal, Kalkajaka and the Hope Islands national parks are managed jointly by the Eastern Kuku Yalanji people and the Queensland Government since the handover.
NASA Earth Observatory image by Joshua Stevens, using Landsat data from the U.S. Geological Survey. Story by Adam Voiland.